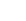MPO (Multi-Position Optical) and MTP® (Multifiber Termination Push-on) Connectors are essentially the same, with MTP® being a branded version of MPO. Both are designed for ribbon cables with multiple fibers, suitable for single-mode and multi-mode applications, and use a push-pull latch for secure connections. Correct cable configuration is crucial to maintain proper signal polarity.
The MT (Mechanical Transfer) Ferrule and MPO Connector technologies were pioneered by NTT in Japan in the early 1980s. These connectors feature a floating ferrule in a plastic housing, replacing less durable silicon chip connections. NTT's advancements led to the MPO standard by 1991, with US Conec enhancing it into the MTP® in 1992. These connectors are now pivotal for high-density, high-bandwidth applications in data centers and computing due to their support for parallel optical transceivers.
The MT Ferrule, central to MPO/MTP® Connectors, is made from glass-filled polymer, allowing for multiple fibers (12 to 16) to be terminated simultaneously. MTP® Connectors introduced metal pin clamps for better pin retention compared to the original plastic clamps of MPO. Both have become standard in network infrastructures, with MTP® innovations setting benchmarks for MPO Connectors.
MPO/MTP® Connectors support 12 to 32 fiber counts, crucial for high-density network cabling systems, facilitating 40G and 100G parallel lane connectivity. They are essential in data centers for their high-speed data transmission capabilities, low insertion loss, and durability.
Key Features of Multi-Position Connectors
- High-speed data transmission, up to 400 Gbps.
- High density connection in a small form-factor, supports multiple fiber ribbons.
- Low insertion loss, less than 0.5 dB, for maintaining signal integrity over long distances.
- Durable for frequent connection and disconnection.
Standards like IEC 61754-5 for MT ferrules and IEC 61754-7 for MPO formats, along with TIA-604-5 and -18 standards define these connectors. Notably, different MPO versions have varying spring force requirements (1 row or 2 rows) and physical dimensions that prevent mismatching, such as between 12F and 16F connectors.
While MPO/MTP® Connectors offer space-saving benefits over alternatives like SC Connectors, they pose challenges in cleanliness and termination due to the high fiber count. The termination process involves ribbonizing fibers and precise polishing, which must be done under controlled conditions, as field repairs are not feasible.
Assembly of these connectors require specific equipment and processes. Fiber Optic Center provides all the industry recommended materials and equipment designed specifically for MPO/MTP® assemblies. Integrating our manufacturing knowledge into our customers’ worldwide operations begins with the best practices and selections listed here:
The versatility of the MT Ferrule extends to specialized applications in aerospace, military, and outdoor environments, where they meet increasing bandwidth needs.
This article is an original publication of Fiber Optic Center, Inc. It is shared publicly for educational and reference purposes to support learning and professional development within the fiber optics industry.
You are welcome to read, cite, or reference this material for non-commercial and educational purposes, as long as full credit is given to Fiber Optic Center, Inc. and the author.
Reuse, reproduction, or adaptation of this content — including rewriting, republishing, or incorporating it into new materials (such as websites, blogs, marketing text, technical guides, or AI-generated content) — is not permitted without prior written consent from Fiber Optic Center, Inc.
This material is protected by copyright law upon publication, even if not formally registered.
Use of this content for AI training, automated data extraction, or derivative content generation is prohibited.
Fiber Optic Center monitors and enforces the integrity of its intellectual property through digital identifiers and content tracking.
For more details, please refer to the Fiber Optic Center Content Use and Copyright policy.